Poor air quality is the largest environmental risk to public health in the UK, as long-term exposure to air pollution can cause chronic conditions such as cardiovascular and respiratory diseases as well as lung cancer, leading to reduced life expectancy. Land-use planning can play a critical role in improving local air quality. At the strategic level, spatial planning can provide for more sustainable transport links between the home, workplace, educational, retail and leisure facilities, and identify appropriate locations for potentially polluting industrial development. Ideally, air quality should be a prime consideration for long term planning, so that land is used and allocated in ways that minimise emissions and that reduce the exposure of people to air pollution. This section provides advice and guidance for developers and planning teams on obligations and opportunities to mitigate for air pollution in the design of local residential, town centre and commercial developments.
Use the filters to narrow down your search
Show more
Active Design Guidance Sport England
Active Design is a combination of 10 principles that promote activity, health and stronger communities through the way we design and build our towns and cities. In partnership with Public Health England, Sport England have produced the Active Design Guidance which works as a step-by-step guide to implementing an active environment. This guidance builds on the original objectives of improving accessibility, enhancing amenity and increasing awareness, and sets out the 10 principles of Active Design.
Download about "Active Design Guidance Sport England" (PDF 15 MB)

Design Council – Healthy Placemaking Report
This Design Council report is focused on healthy placemaking. It examines the barriers identified by people building and designing our communities to creating places where people are healthier and happier. Great design is changing the way we live and the places we live in, making lives better by building happier, healthier and safer environments. It can bring communities together and facilitate long term behaviour change, transforming our lifestyles for the better
Download about "Design Council – Healthy Placemaking Report" (PDF 721 KB)

The role of active travel in Improving Mental Health Pt 3
This is the third part of the Active Travel toolkit on The Role of Active Travel in Improving Health
Download about "The role of active travel in Improving Mental Health Pt 3" (PDF 303 KB)

Creating healthy places Perspectives from NHS England’s Healthy New Towns programme
The places we live in and the communities we belong to affect our health in countless ways – sometimes very visibly, sometimes more subtly, but with a significant combined effect. A coherent approach to improving population health therefore needs to include a focus on places, neighbourhoods and communities as well as interventions aimed at individuals and at the whole population (Buck et al2018).

NICE Air Quality Standards
NICE quality standards describe high-priority areas for quality improvement in a defined care or service area. Each standard consists of a prioritised set of specific, concise and measurable statements. NICE quality standards draw on existing NICE or NICE-accredited guidance that provides an underpinning, comprehensive set of recommendations, and are designed to support the measurement of improvement.

Active Travel Strategic Investment Tool Guidance
The primary purpose of the SUSTRANS Strategic Investment Tool (SIT) is to help local authorities and local enterprise partnerships develop large scale programmes of investments in active travel. Using evidence from the evaluations of a wide range of active travel interventions the SIT calculates the typical impact and cost of an investment programme consisting of a range of different intervention types.
Download about "Active Travel Strategic Investment Tool Guidance" (PDF 510 KB)

Active Travel and Economic Performance slides
A ‘What Works’ review of evidence from cycling and walking schemes published by Sustrans
Download about "Active Travel and Economic Performance slides" (PDF 460 KB)

Introduction to the Green Infrastructure Framework
“Good quality Green Infrastructure (GI) has an important role to play in our urban and rural environments for improving health and wellbeing, air quality, nature recovery and resilience to and...
Read more about "Introduction to the Green Infrastructure Framework"
Natural England: Green Infrastructure Mapping Tool
Natural England's Green Infrastructure (GI) Map allows users to view information on the type and location of GI, with easy-to-use filters allowing specific types of infrastructure to be selected, and additional datasets - such as deprivation indices, population density, demographics and health information - to be overlaid. The tool can assist in identifying gaps and opportunities to support policy and development decisions linked to green infrastructure.
Read more about "Natural England: Green Infrastructure Mapping Tool"

The 20-Minute Neighbourhood (TCPA)
Around the world there is growing interest in creating places in which most of people's daily needs can be met within a short walk or cycle. The benefits of this approach are multiple: people become more active, improving their mental and physical health; traffic is reduced, and air quality improved; local shops and businesses thrive; and people see more of their neighbours, strengthening community bonds.

Mental Health and Town Planning
In the UK and Ireland, the rates of mental health illness are high. Where someone lives can have an impact on their mental health. The quality of the wider built environment is also a determining factor for mental health, with noise, pollution levels, quality of green space, access to services and even ‘beauty’ all playing a part. This practice note gives advice on how planners can work within the current UK planning systems and with other professionals to take account of mental health when making changes to the built environment.
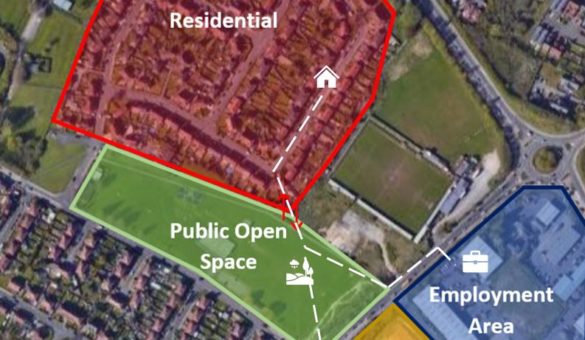
Creating Attractive and Effective Connections (Part Two)
This case study expands upon Creating Attractive and Effective Connections (Part One) by looking at an additional example of how to consider the quality and potential impact of connections across...
Read more about "Creating Attractive and Effective Connections (Part Two)"

Improving Air Quality Walking Cycling
This is the second part of the Active Travel toolkit on The Role of Active Travel in Improving Health The Active Travel toolkits aim to help LEPs and their local delivery partners to: 1 Develop your business case for investment in walking and cycling schemes. 2 Link walking and cycling schemes to your strategic economic growth priorities, housing growth and planning, and public health. 3 Support the planning and delivery of walking and cycling schemes in your local area.
Download about "Improving Air Quality Walking Cycling" (PDF 450 KB)

RTPI Enabling-Healthy-Placemaking Research Paper
This RTPI research paper explores local, national and international planning practices enabling the creation and delivery of healthy places.
Download about "RTPI Enabling-Healthy-Placemaking Research Paper" (PDF 951 KB)

Active Travel and Economic Performance SUSTRANS
Active Travel and Economic Performance A ‘What Works’ review of evidence from cycling and walking schemes
Download about "Active Travel and Economic Performance SUSTRANS" (PDF 543 KB)

National Planning Policy Framework (2021)
The National Planning Policy Framework sets out the Government’s planning policies for England and how these should be applied. It provides a framework within which locally-prepared plans for housing and other development can be produced.
Download about "National Planning Policy Framework (2021)" (PDF 536 KB)
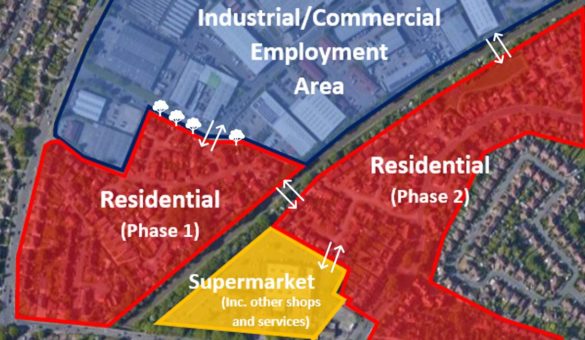
Creating Attractive and Effective Connections (Part One)
Walkable communities provide an opportunity to encourage active travel – whether that be walking, cycling or scooting – by connecting a range key places (such as homes, shops, schools, workplaces...
Read more about "Creating Attractive and Effective Connections (Part One)"

